As the landscape for asset management continues to quickly evolve, data has emerged as one of the cornerstones for driving reliability and maintenance, efficiency, and effectiveness. For reliability professionals and asset managers, leveraging asset data and information is not merely a trend but a necessity.
Instead of drowning in data and starving for information, we can now transform data into information that gives decision makers knowledge and actionable insights. This can enhance organizational decision-making, enable optimized asset performance, and increase the longevity and reliability of assets and complex equipment.
The Role of Data in Maintenance Strategy
Asset data encompasses a wide array of information from asset and maintenance records to operational metrics, historical performance, and current operating context.
Accessing accurate and timely data and interpreting the resulting information enables reliability professionals to pre-empt equipment failures, reduce downtime, and plan maintenance activities more effectively. Furthermore, these data-driven insights can highlight inefficiencies and opportunities for improvement, leading to significant cost savings and increased asset availability.
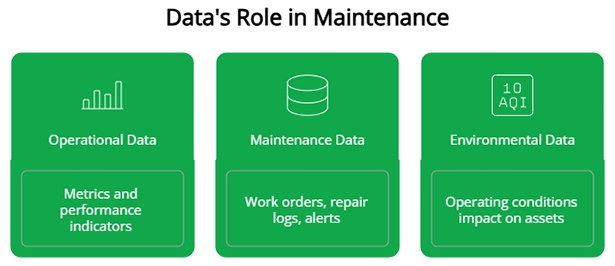
Key Operating Context Data
- Operational Data: metrics and performance indicators such as uptime, production output or throughput, production defects or off-spec rates, and operational efficiency, etc.
- Maintenance Data: work order histories, repair logs, and predictive maintenance alerts, etc.
- Environmental Data: operating conditions such as temperature, pressure, humidity, exposure to corrosive or erosive fluids, etc.
Capturing the Right Data at the Right Time
Harnessing asset data to support decision making starts with acquiring and integrating the data itself. Reliability professionals need robust systems and tools to capture data from various sources, such as IoT devices and sensors, manual record logs, and work order systems.
Centralized, consistent data is the backbone of reliable decision-making.
Integrating this from disparate data sources into usable information is key to integrating it into a centralized platform or a single point for access. This enables all stakeholders access to up-to-date, consistent, and accurate data for analysis and decision making. Older practices of everyone having their own personal database or spreadsheets are rife with the potential for incomplete and inaccurate data and information, missing assets, and an inability to share analysis results.
Leading Practices
- Deploy IoT Solutions: Utilize sensors and smart devices to gather real-time data on asset performance. These new and emerging technologies enhance data acquisition and sharing to drive innovation in data analytics.
- Centralized Data Management: Adopt a centralized platform or data access point that integrates data from various diverse sources. This ensures a unified source of truth.
- Data Quality Assurance: establish and follow regular data validation and cleansing processes to enable access to up-to-date and accurate data.
Visualizing Trends to Drive Better Decisions
Once the data has been collected and integrated from many sources, the next step is to analyze it. We are moving from ‘drowning in data and starving for information’ to ‘accurate and up-to-date data leading to information leading to knowledge to enable our decisions.’
We’re not drowning in data—we’re visualizing it into decisions.
One of the easiest ways to improve our analysis is to be able to visualize it. This means charts, tables, graphs, and dashboards that enable reliability practitioners to see and uncover patterns, predict future trends, and anticipate asset performance under various operating conditions. Recent advances in AI make this type of visual analytics easier and faster to perform. These visualizations of the data also make it far easier to communicate with stakeholders who may not be as familiar with the intricacies of reliability analytics or equipment performance.
Leading Practices
- Predicative analytics: This includes using algorithms to forecast potential component or equipment failures and thus schedule repair or preventive maintenance intervals.
- Real-time dashboards: This includes developing and publishing dashboards that display real-time data, enabling prompt and informed decision-making.
- Trend analysis: This includes historical data analysis coupled with current and expected future operating conditions to identify long-term trends and provide input for organizational strategic planning.
Data-Driven Maintenance for Maximum Asset Uptime
Using up-to-date data, information, and analytical results is the key to extending the asset lifespan and ideally, minimizing downtime and maximizing equipment availability.
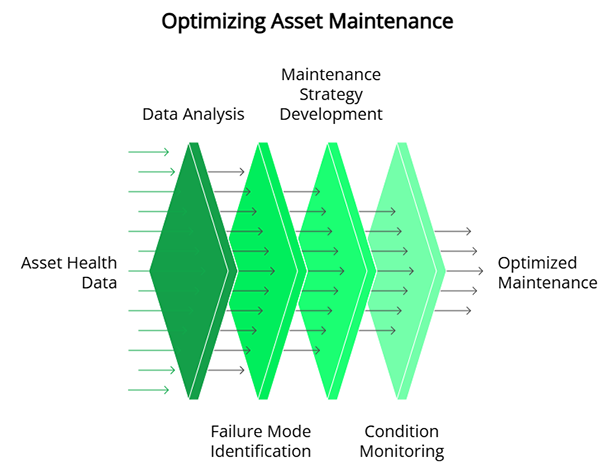
When we think about implementing maintenance strategies for more critical assets developed through techniques like reliability-centered maintenance (RCM), failure modes and effects criticality analysis (FMECA), or optimized using PM Optimization (PMO), there is a heavy emphasis on performing the right activities at the right intervals.
Reliability professionals set those intervals using historical data analytics while monitoring asset health parameters to decide the best timing for repairs, restoration, or other interventions.
Leading Practices
- Failure Mode Analysis—Identify common failure modes as part of an RCM, FMECA, or PMO analysis and then implement the associated preventive, predictive, or failure-finding task measures. Reliability professionals use data insights to inform the choice of maintenance activity and/or intervals and for periodic reviews.
- Condition-based Monitoring (CBM) monitors asset health performance and conditions in real time and performs maintenance activities when specified thresholds or alarm parameters are met.
Establishing Trust Through Data Governance
While the recent improvements in data access from anywhere at any time are enormously important to reliability professionals who are working diligently to improve asset performance, there are risks associated with this access.
It is important to consider the integrity, privacy, and security of the data we now rely upon. Data governance involves establishing and implementing policies, standards, processes, and practices to manage our data effectively.
Leading Practices
- Data Governance Framework: Establish and implement a comprehensive framework for all data governance, including policies, standards, processes, procedures, and practices.
- Data Access Controls: Identify and implement role-based access to data and control who can view and edit it.
- Cybersecurity: establish and implement encryption, firewalls, authentication, and other security measures to safeguard data. This is not a one-and-done exercise but a critical ongoing activity.
Asset Data as a Strategic Advantage
The world of data and data analytics continues to evolve quickly. It is one of the cornerstones for driving reliability, maintenance efficiency, and effectiveness.
As organizations take advantage of emerging technology, it can drive step-change improvements in overall reliability outcomes, leading to increased equipment availability and reduced costs. Data thus becomes one of the foundational inputs that organizations can use for strategic advantage.